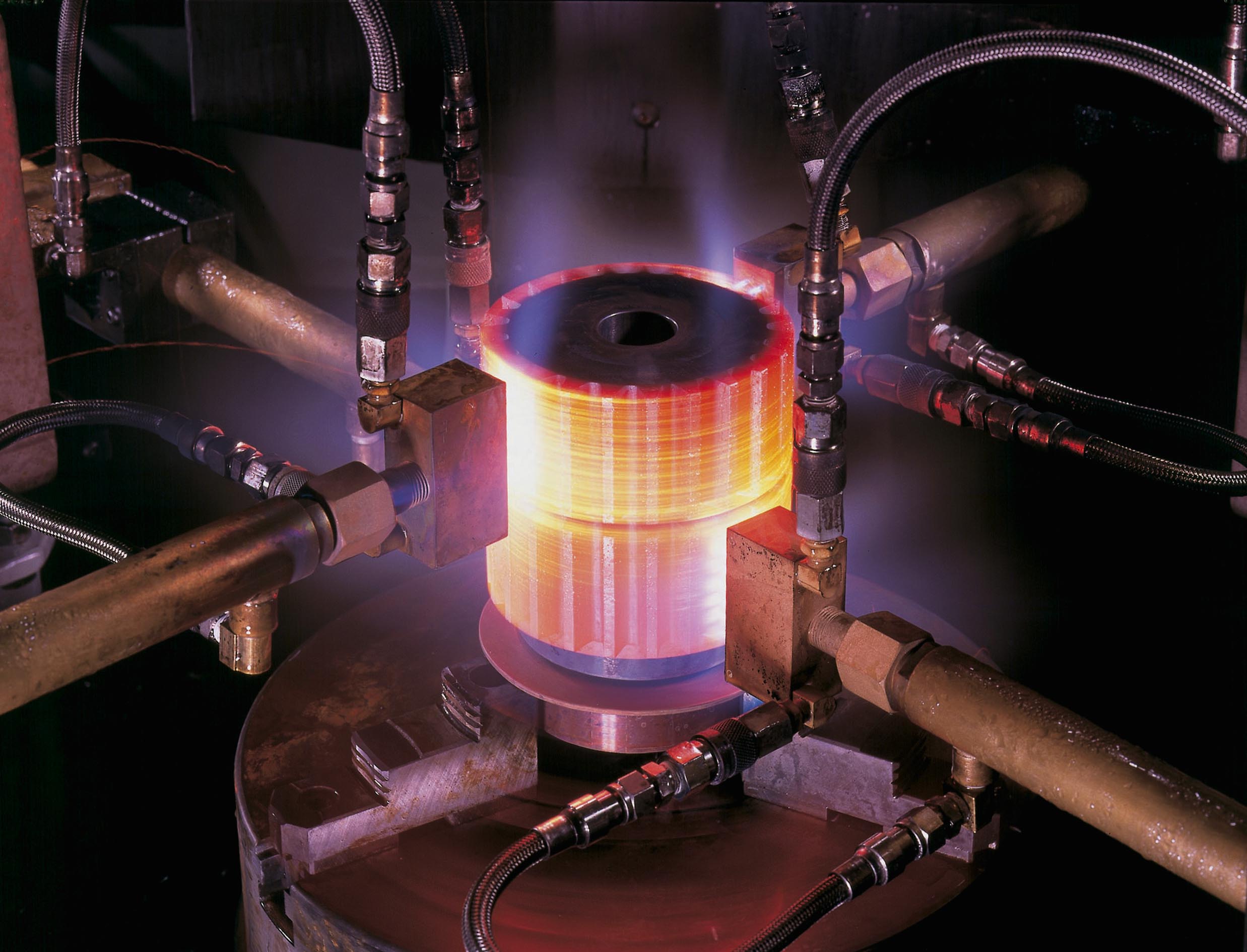
This process follows three main steps, and each must be followed correctly for the best outcome:
Heating: Here, the metal you’re working with is heated to a certain temperature. The temperature used depends on the metal.
Holding: This is when the workpiece is kept at the set temperature for a while, allowing it to spread evenly throughout the part.
Cooling: The metal is then cooled in a controlled way, which affects the internal structure.
The cooling speed also affects how hard the metal turns out. If it is done rapidly, the part becomes very hard, while if it’s done slowly, it makes the metal soft. The heating environment, whether it’s air, vacuum, salt bath, or gas, all serve different purposes.
Salt baths ensure the metal parts are heated evenly, while a vacuum space helps prevent unwanted reactions.